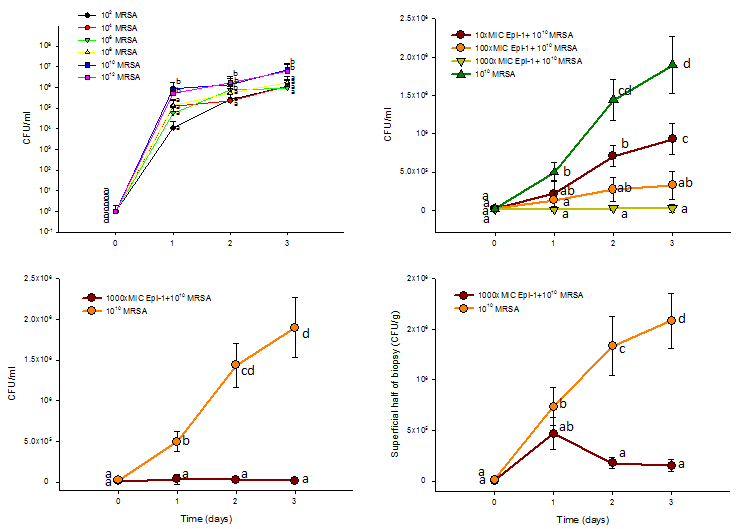
Epi-1 decreases the heat injury-mediated MRSA infection in pigs
Three-centimeter-diameter heat injury wounds were generated using a heated aluminum bar after the pigs were fasted overnight and sedated. A MRSA suspension in 0.5 ml of saline was used to inoculate the wounded region. The wounded area was thoroughly washed before sampling, and then samples were collected. (A) Wounds infected with MRSA alone at 102 to 1012 CFU/0.5 ml. MRSA counts (CFU/ml) were calculated 1, 2 and 3 days post infection. (B) At six hours post infection with 1010 CFU MRSA, the wounds were treated with Epi-1 concentrations equivalent to 0 (PBS only), 10 (90 g/ml), 100 (900 g/ml), 1000 (9 mg/ml)-fold of the MIC for MRSA for 1 h. Subsequently, the MRSA counts were estimated in surface wash sample concentrates. (C) Bacteria counts in the surface wash concentrates. (D) Concentrations of bacteria in the superficial and deep layers of the biopsies.
Epi-1 enhances wound healing activities in skin wounds
Histological sections collected at the time of infection and various time points after infection were sectioned and stained with H&E, and the formation of the epithelial layer during the healing process was visualized. (A) Enhanced vascularization was observed in the Epi-1-treated sections. (B) Increased Notch activity was observed in epithelial cells from the Epi-1-treated samples.
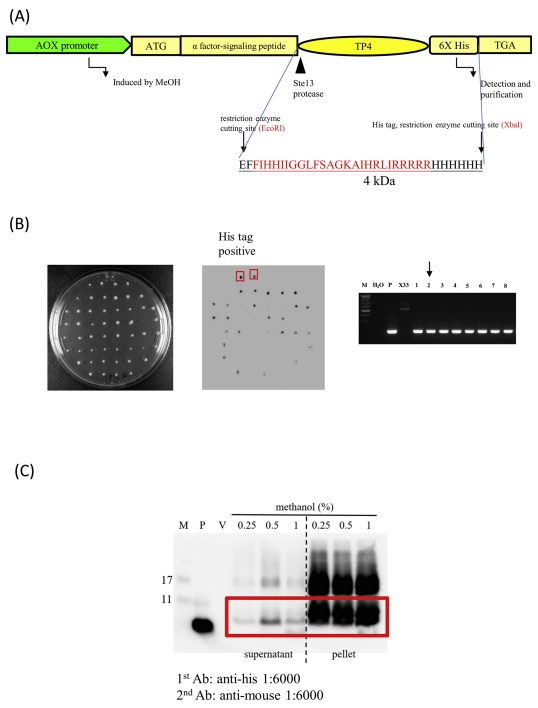
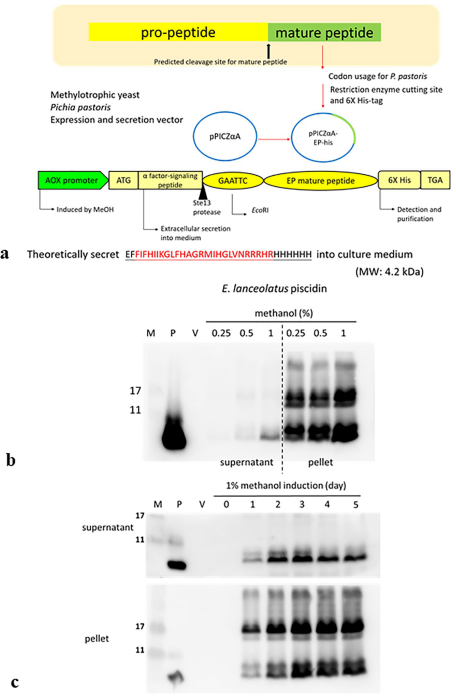
Recombinant TP4 can be expressed in yeast.
(A) The expression cassette contains a TP4-encoding DNA sequence, which was synthesized and inserted into the pPICZα vector. (B) Expression of rTP4 was confirmed by colony hybridization with a His-specific antibody. PCR was used to verify that the yeast clones contained the TP4 cDNA insert. P: positive control, insert was used as template. × 33: control without TP4 cDNA insert. (C) Immunoblotting showed that methanol can induce expression of rTP4 in yeast. Divided into two groups. After methanol induction, supernatant and pellet were probed by western blot determine the expression of rTP4 protein in yeast.
Epi-1 enhances the formation of collagen structures at the healing wound site
Histological sections were collected at the time of infection and various time points after infection, sectioned, and subjected to Masson’s trichrome staining to visualize collagen formation. (A) The Epi-1-treated wounds showed an improvement in the deposition of the collagen layer. (B) The deposition of the collagen layer in the Epi-1-treated samples was superior to the samples treated with the currently available MRSA antibiotic Vancomycin.
AMP多元應用。
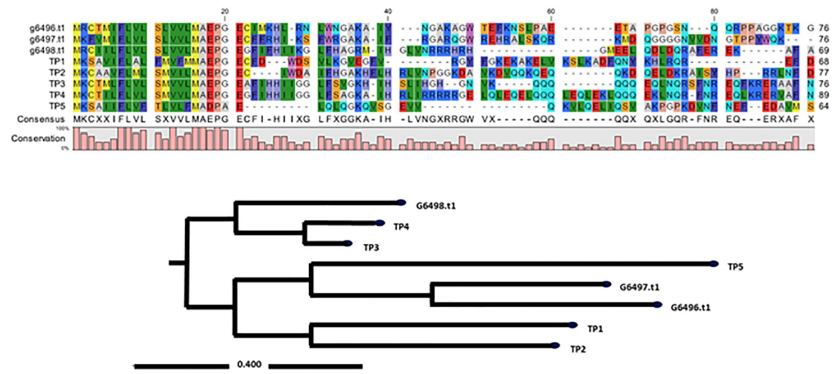
Sequence alignment of tilapia piscidins and Epinephelus lanceolatus piscidins.
Multiple sequence alignments of the tilapia piscidin peptides with isolated E. lanceolatus piscidins (g6496.t1, g6497.t1 and g6498.t1). Gaps were inserted to obtain maximum homology. All coding sequences were input into the dendrogram for alignment. The same amino acid is indicated by the same color, e.g., methionine (M) is indicated by yellow. The result of a phylogenetic analysis of piscidins from tilapia (TP1 to TP5) and E. lanceolatus is shown.
Expression of the E. lanceolatus piscidin-6×His (rEP) protein in Pichia pastoris.
(a) Plasmid map of the pPICZαA-EP-his vector. (b) Different concentrations of methanol were used for induction, and recombinant protein expression was analyzed by western blotting. (c) Cells were harvested and total protein from supernatant and pellet were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting. Lane 1, low-range rainbow marker; lane 2, synthesized EP; lane 3, protein expressed by the pPICZαA vector; lane 4–9, cells containing EP expression vector after induction for 0 h (no methanol induction), 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 days.
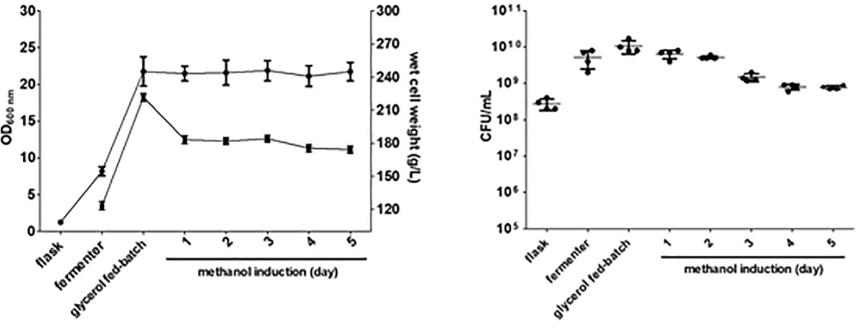
rTP4 in yeast was expressed in a bench-top fermenter under optimized conditions.
(A) Graph shows temperature (°C), RPM, pH and dissolved Oxygen (DO) conditions during the growth phase (1 day) and after methanol induction (5 days). The following parameters were found optimal for the 5000-ml bench-top fermentation tank: 30 °C, 800 RPM, pH 6.0, > 2 volumes of air per volume of batch per minute (vvm). (B) Yeast cultured for 5 days was treated with 2 % methanol to induce production of rTP4. 6×His-tagged rTP4 in supernatant and pellet was analyzed by immunoblot with an anti-His antibody. Synthetic TP4-6×His (P) (50 ng) was used as a reference. The quantity of rTP4 relative to P is displayed in the box. M: molecular weight marker. V: vector alone without TP4 insert in P. pastoris. (C) analysis of TP4-transformants grown in the fermenter at different stages. The OD 600 and wet cell weight (g/L) are shown. After methanol induction, yeast growth was better using the flask method compared to the fermenter method.

Epi-1 increases the recruitment of leukocytes near the injury region to accelerate wound healing
Histological sections were collected at the time of infection and various time points after infection, sectioned, stained with Giemsa, and neutrophil recruitment was visualized. Sections from the Epi-1-treated samples showed an increase in the number of neutrophils near the infected region.
Epi-1 promotes complete skin regeneration of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-infected
1. We have demonstrated that Epi-1 exerts potent
antimicrobial activity against methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus (a MDR clinical isolate). The use
of Epi-1 may complement the use of antibiotics. AMPs are
unlikely to induce resistance.
2. Treatment with Epi-1 significantly reduces MRSA
infection in a mouse model of wound infection compared
to untreated controls and mice treated with conventional
antibiotics. Given the prophylactic efficacy of Epi-1
and its inability to engender resistance, this AMP may
be suitable for situations in which there is a high risk of
infection.
3. Our model is valuable for future research on
the pathophysiology of wound healing and testing new
therapeutics for the treatment of bacterial infections during
wound healing.
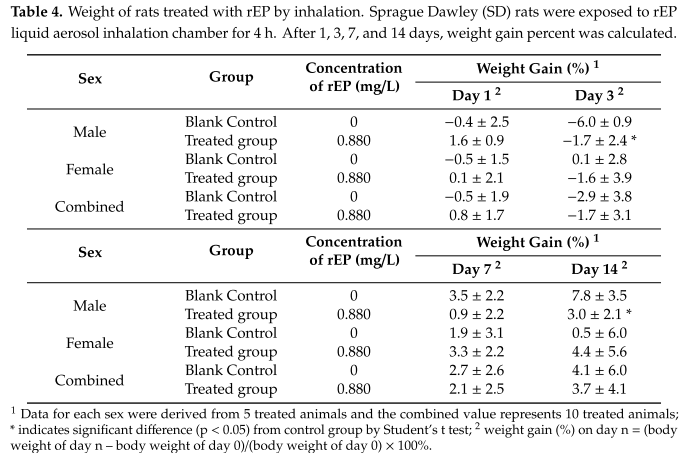
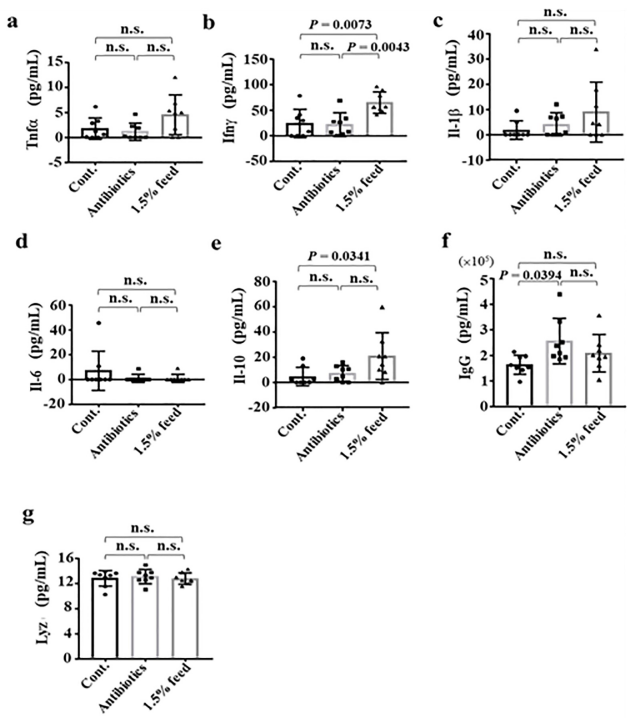
Effects of rEP administration in chicken were evaluated by determining the levels of immunological.
Effects of rEP administration in chicken were evaluated by determining the levels of immunological factors,
including immunoglobin G (IgG), Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, Interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-10, Lysozyme
(Lyz), and Interferon (IFN)-γ by ELISA.

Abstract
In this study, we expressed the TP4 peptide, originally identified from Oreochromis niloticus, in yeast (Pichia pastoris) under the control of an alcohol oxidase (Aox) 1 promoter. Recombinant (r)TP4 expression was induced by methanol. Transformation was confirmed by PCR, and expression was confirmed by colony hybridization. For scalable production, transformed yeast was cultured and induced in a bench-top fermenter bioreactor system under controlled conditions. The rTP4-expressing yeast cells were then pelleted and fed to 28-day-old Lates calcarifer as a 0, 1, 3 or 5 % supplement to the normal diet. Furthermore, rTP4-yeast-containing diet elevated SOD, GPx and catalase activities. Since feeding L. calcarifer with bioreactor-produced rTP4-expressing yeast significantly enhanced growth and immunity, rTP4 should be considered for use as a functional feed supplement to replace excessively administered antibiotics in farmed fish.

Epi-1 regulates the CRP and IL-6 expression associated with injury-mediated inflammation and sepsis
Heat wound-injured pigs were infected with MRSA and treated with PBS (control), Vancomycin (0.5 mg/kg body weight) and a 1000-fold MIC of Epi-1 (9 mg/ml) at 6 h post infection. Blood was collected from the vein and immediately processed. (A) Plasma was isolated from the blood and the CRP content was assayed with an ELISA. (B) Serum IL-6 levels were assayed with an ELISA.
石斑魚抗菌肽酵母粉
含基因改造微生物之飼料用產品查驗登記申請書。
本團隊在2020亞太區農業技術展覽暨會議設有展出攤位。
主題:海洋活性抗菌胜肽酵母粉-家禽飼料添加物
時間:11/5(四) - 11/7(六)
地點:台北南港展覽館1館
攤位編號:633/J
歡迎蒞臨指教
Diets supplemented with rTP4-expressing yeast enhance growth in L. calcarifer.
Pellets of transformed yeast expressing rTP4 were mixed into fish meal at 1, 3 or 5 %, and fed to L. calcarifer for 28 days. The morphology and growth performance were monitored. Diet without yeast was used as a control.

Effect of medium composition on the expression of rEP in P. pastoris.
The effect of nutrient content was evaluated by comparing P. pastoris X33 transformant cultures grown in BMGY (flask culture, circles) and BSM (fermenter culture, squares) according to thier wet cell weight and cell counts.
Abstract
Supplementation of feed
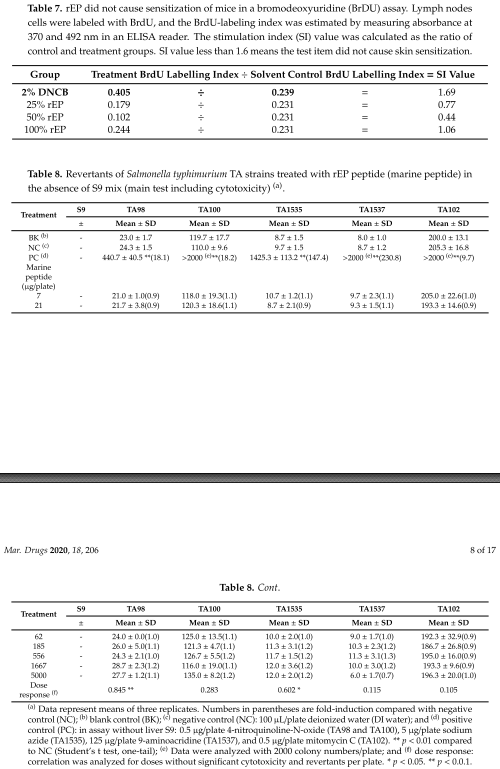
with recombinant Epinephelus lanceolatus piscidin (rEP)-expressing yeast pellets may minimize the excessive use of antibiotics and control pathogens in aquaculture or animal husbandry. However, before implementing rEP as a supplement, it is necessary to understand whether it harbors any toxicity. Since toxicological information on the topic is scarce, the present investigation was carried out to test whether rEP exhibits allergenic and/or toxic effects. The stimulation indexes (SIs) were
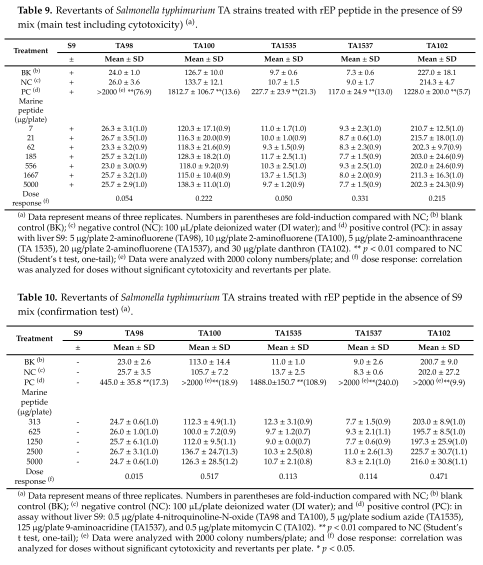
1.06 (100%), 0.44 (50%), and 0.77 (25%), all of which were less than the cutoff value for a positive sensitization result (1.6). Negative response was also seen in the bacterial reverse mutation test (OECD 471), and no chromosomal effects on Chinese hamster ovary (CHO)-K1 cells were observed (OECD 487). Based on these six toxicity tests, rEP showed neither acute toxic effects in experimental animals nor mutagenicity.



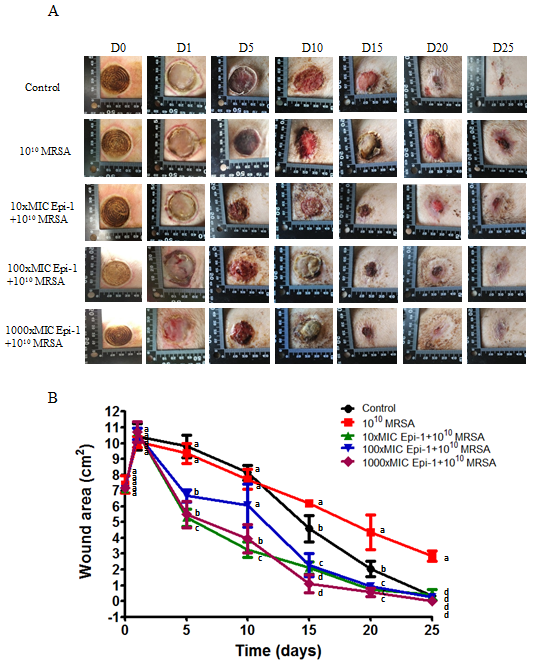
Epi-1 cures MRSA infection in heat burn wounds
Three-centimeter-diameter heat wounds were created with a heated aluminum bar after the pigs fasted overnight and were sedated. A 1010 CFU MRSA suspension in 0.5 ml of saline was used to inoculate the wounded region. The wounded area was thoroughly washed before sampling, and then samples were collected. (A) The MRSA infection-mediated wound healed after treatment with Epi-1 at 6 h post infection. (B) The area of the wound injury was measured at 0, 1, 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 days post infection using photo shot software (Scion, Frederick, MD), and the percentage contraction was calculated by dividing the initial wounding area on day 0 by the wounding area on different days.
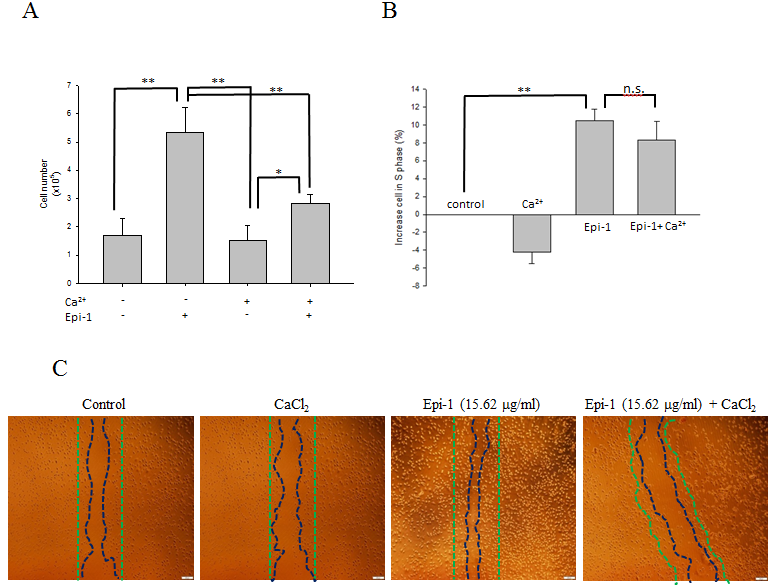
Epi-1 inhibits cell differentiation by extra cellular calcium and increases cell proliferation
(A) Approximately 100,000 HaCaT cells/well cultured in 6-well plates were serum-starved and treated with PBS alone (control), 15.62 g/ml Epi-1 and/or 1.6 mM CaCl2, and the fraction of proliferating cells was assessed by counting the cells in a Countess automated cell counter. (B) The percentage of cells from each group, i.e., PBS alone (control), 15.62 g/ml Epi-1 and/or 1.6 mM CaCl2, in S-phase was obtained using a cytometer. (C) Cells growing in a monolayer were scratched with a P1000 pipette tip to generate an artificial wound and then treated with 15.62 g/ml Epi-1 in the presence or absence of 1.6 mM CaCl2. Cell migration and proliferation in the wounded region was calculated by assessing the photographed image using an image analyzer.
姓名:陳志毅
職稱:研究員
電話: 03-9880544 ext.15
專長:Antimicrobial peptides, Marine biotechnology

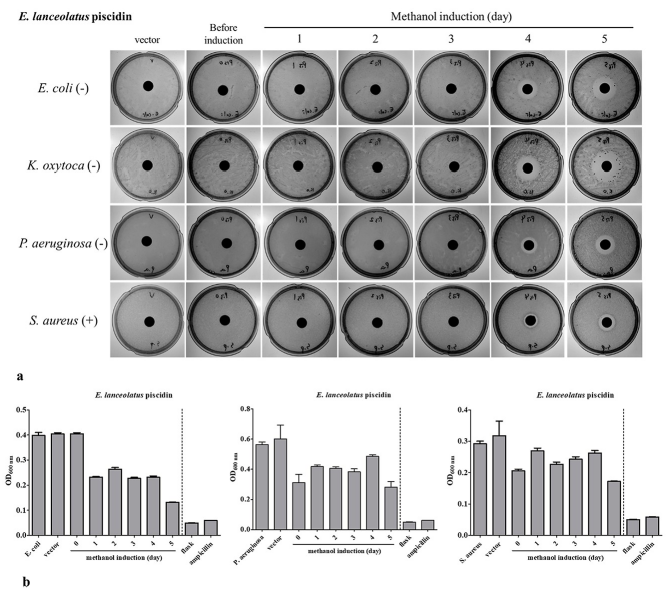
Antimicrobial activity of rEP produced in P. pastoris by flask and fermenter methods.
(a) rEP concentration in the yeast culture supernatant before and after induction with methanol for 24 h to 120 h in flask culture. After 5 days of induction, yeast culture supernatant produced large inhibition zones, ordered by width, for K. oxytoca, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus. The marker “-” represents Gram-negative; “+” represents Gram-positive. (b) The
antibacterial activity of rEP produced by the fermenter method. Yeast were induced with methanol from 24 h to 120 h in a fermenter. The supernatant showed inhibitory activity toward E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus, as measured by OD 600 . The flask supernatant exhibited greater antimicrobial activity compared to fermenter supernatant.
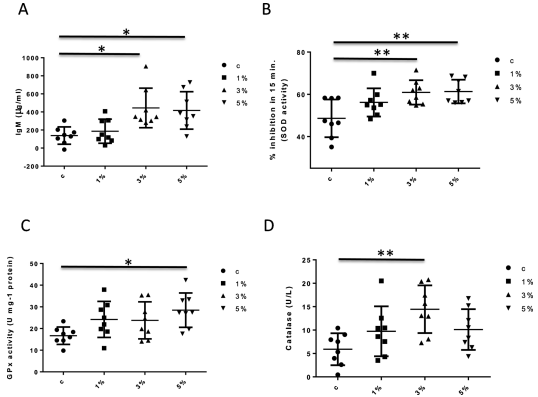
rTP4-expressing yeast supplementation of fish meal enhances immune activities in L. calcarifer.
The pellets of transformed yeast expressing rTP4 were mixed into fish meal at 1, 3 or 5 %, and fed to L. calcarifer for 28 days. The levels of Immunoglobulin M (IgM), and SOD, GPx and Catalase
activity were measured. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
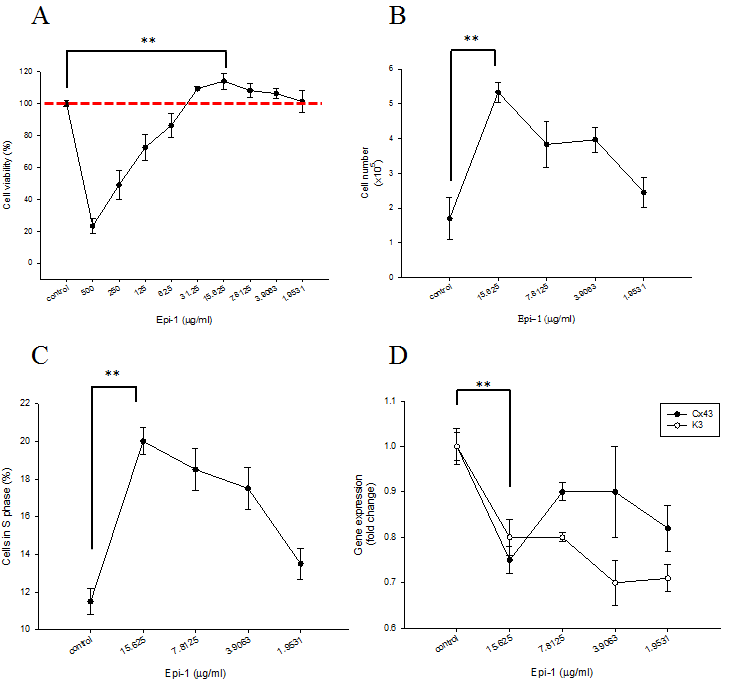
Epinecidin-1 (Epi-1) increases keratinocyte proliferation
HaCaT cells were serum starved overnight. Subsequently, the cells were treated with 0 to 500ug/ml Epi-1 for one hour, and then cultured with normal cell culture medium for 48h.(A)A cell viability assay was conducted with 20,000cells/well seeded in a 96-well plate that had been treated with the PBS control or Epi-1 at 500ug/ml and two-fold serial dilutions to 1.9531ug/ml for 1h.(B) Cells were seeded in 6-well plates at a density of 100,000 cells/well and treated with the PBS control or Epi-1 before counting. (C) Cells that had been cultured in six-well plates and treated with or without Epi-1 were harvested, stained with propidium iodide, and subjected to flow cytometry to detect the percentage of S-phase cells. (D) Total RNA was isolated from the cells that had been cultured in six-well plates and treated with or without Epi-1 and was used for the RT-PCR analysis to detect the expression of the differentiation marker K3 and Cx43.

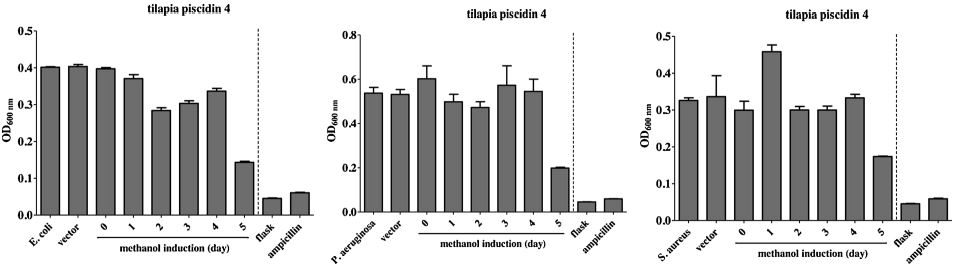
Supernatant of yeast expressing rTP4 exhibits antimicrobial activity.
Samples of about 50 μl were collected daily from the fermenter with yeast expressing rTP4, and the supernatant and pellet were separated by centrifugation. The volume of supernatant was topped off to 50 μl with fresh medium. The supernatant was then mixed with equal volume of diluted bacteria and incubated overnight to allow bacterial growth. After 24 h, bacterial growth was assessed by
measuring OD 600 . The supernatant of flask-grown yeast expressing rTP4 was also assessed, and ampicillin served as a positive control. The bacterial strains,
Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Sachcharomyces aureus, were prepared by culturing to OD 600 = 0.8–1.0 and then diluting 1000-fold prior to mixing with supernatant.
Abstract
Supplementing chicken feed with antibiotics can improve survival and prevent disease outbreaks. However, overuse of antibiotics may promote the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Here, we evaluate the effects of antimicrobial peptide, Epinephelus lanceolatus piscidin (EP), in Gallus gallus domesticus. The expressed recombinant EP (rEP) was then used as a dietary supplement for G. g. domesticus; overall health, growth performance and immunity were assessed. Treatment groups included control, basal diet and rEP at different doses (0.75, 1.5, 3.0, 6.0 and 12%). Compared to control, rEP supplementation increased G. g. domesticus weight gain, feed efficiency, IL-10 and IFN-γ production. Our results suggest that crude rEP could provide an alternative to traditional antibiotic feed additives for G. g. domesticus, serving to enhance growth and health of the animals.